Snake bite
02 MAY 2011
Snake bite - Complication
Dr.Prem Sankar Pandyan -MEM PGY 1
Dr.Abdul Jaleel PM MEM PGY 3
A 28 yr old lady brought unconscious to ED at 7.30 am with history of alleged snake bite 3 days back...
Airway-Patent
Breathing-tachypnea
Circulation-capillary refill >2 seconds
Disability-unconscious,pupils dilated sluggish to light
Exposure-Eccymotic patches+
Bite mark Rt ankle+
Cellulitis Rt leg+
vitals
Pulse-168/mt
Bp- 80/60 mm of hg
Temp-102 F
Spo2-100% in room air
GRBS-110 mg/dl
Sign & symptoms
Hemetemesis and hematuria
Progressive worsening of sensorium and breathing difficulty
Allergies- Nil specific
Medications-Nil
Past medical history-Nil
Last meal-3 days back on 30.03.11 at 7 am
Event-
Snake bite on 30.03.11 at 7.30am
On examination-
HEENT-pupils dilated,sluggish
Cardiovascular system-S1 S2 +, no S3,no gallop
Respiratory system-BAE +
Gastrointestinal system –within normal limits
Extremities-Bite mark Rt ankle +,cellulitis +, Multiple stones were put and packed on bite mark and incised wounds near to bite marks
Spine and back-within normal limits
Nervous system-unconscious,rigid,plantar to upwards,DTR-negative
Diagnosis: SNAKE BITE POISONING(VIPER) WITH COAGULATION FAILURE
Investigations-
HB-10.4 MG/DL
TOTAL WBC-21800
PLATELET COUNT-15,000
BT-2.3O MTS
CT-13 MTS
PT-13.9 SEC ,CONTROL-12 SEC
INR-1.21
APTT 27.0 SEC
UPT-NEGATIVE
CPK TOTAL-9920 U/L
S.UREA-34
S.CREAT-0.7
BILIRUBIN TOTAL-3.6 MG/DL
BILIRUBIN CONJUGATED 0.4 MG/DL
SGOT-524
SGPT-136
URINE ROUTINE- RBC +++
ELECTROLYTES –WITHIN IN NORMAL LIMITS
ABG - WITHIN IN NORMAL LIMITS
IMAGING-CT BRAIN
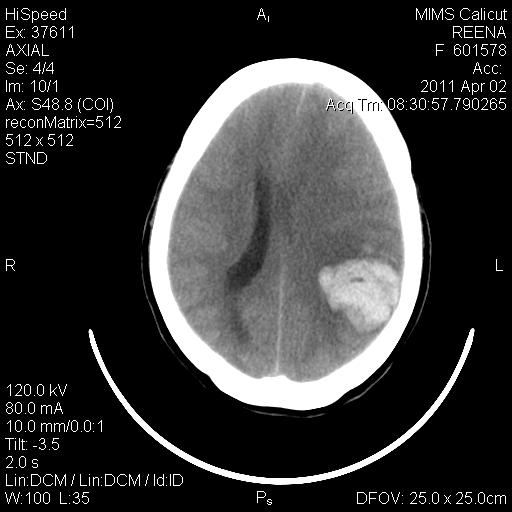
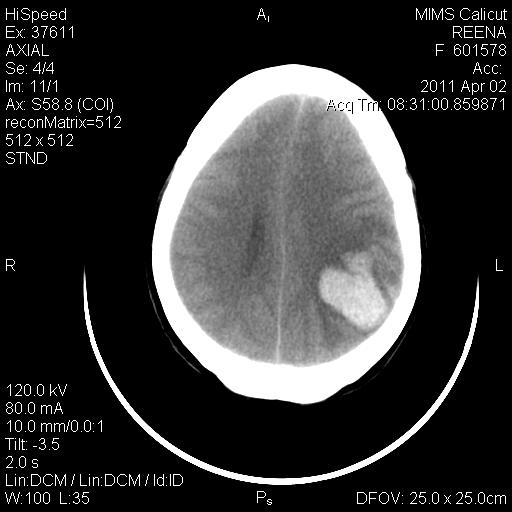
Left tempero parietal haematoma 4.1 cm x 3.5 cm with mass effect and midline shift of about 9 mm
Management-
Intubation and mechanical ventilation
Anti snake venom
Broad spectrum antibiotics
Anticonvulsants
Platelet transfusions
Ionotrophic supports
And other supportive measures.
Neurosurgery consultation.
Neurolgy consultation.
Surgery consultation.
DISCUSSION
Identification
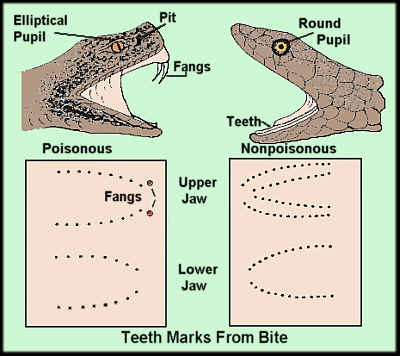
The above figure shows the difference between poisonous and non poisonous snakes.
Toxins : The following tabular column shows the components of toxins.
Components
Examples
Nonprotein Compounds (5–10%)
Metals
Copper, zinc, sodium, magnesium
Free amino acids
Glycine, valine, isoleucine
Peptides
Pyroglutamylpeptide
Nucleosides
Adenosine, guanosine, inosine
Carbohydrates
Neutral sugars, sialic acid
Lipids
Phospholipids, cholesterol
Biogenic amines
Spermine, histamine, serotonin
Protein Components (90–95%)
Enzymes
Proteolytic enzymes, collagenases, phospholipase A, nucleotidase, hyaluronidase, acetylcholinesterase, amino acid oxidase
Polypeptides
Crotoxin, cardiotoxin, crotamine
Clinical features:
Bleeding from gums,GIT
Hematuria,heavy protenuria
Hemodynamic abnormalities (hypotension,tachycardia,shock)
Epigatric and renal angle pain
Periorbital oedema
Regional lymph node enlargement and pain
Laboratory evaluation:
Prothrombin time*
Creatine kinase level
Partial thromboplastin time*
ECG
Fibrinogen level*
Arterial blood gas analysis‡
Fibrin degradation product levels
Serum electrolyte levels
Glucose level
Blood urea nitrogen level
Treatment:
Prehospital:
Retreat well beyond striking range. Many victims are bitten again while trying to capture the snake.
Remain calm. Movement will increase venom absorption.
Immobilize the extremity in a neutral position below the level of the heart.
Ensure prompt transport to a medical facility whether or not there are signs of envenomation.
Constriction bands can be applied if there is no nearby medical facility.
Suction and incision are dangerous and should not be done.
Use of tourniquets are contraindicated
Constriction bands can be used but loose enough that a finger can slide beneath.
First aid:The following tabular column shows the first aid to be done
In hospital treatment:
Antivenom administration depending upon the severity of envenomation
Envenomation
FabAV[†]
Wyeth AV
Moderate
4–6 vials
4–6 vials
Severe
8–12 vials
5–10 vials
Very severe
12–18 vials
10–20+ vials
Broad spectrum antibiotics.
Platelet and blood transfusions.
Anti convulusants,Vassopressors if needed.
Wound care.
other supportive measures.
Awareness:
Learning and teaching ‘snake awareness’ to the public,
Be aware of the dangers posed by snakes and take steps to avoid them.
As far as you are able, ‘proof’ your home and garden against snakes.
Know the symptoms of a snake bite and the appropriate treatment.
Take the patient to the nearby hospial as soon as possible.
Making incision near to bite mark and putting stone will lead to more absorption of venom and expose to multiple microbes
MYTHS IN SNAKE BITE TREATMENT IN KERALA
Visha Vaidya
Visha Vaidya is one branch of traditional healing, popular in Kerala, mostly in Palakad and Trichur, involving treatment of poisonous bites like that from snake, dog and stings of scorpion, spider etc. Visha Vaidya deals with management of poisonous bites, poisonous substances and their action, Antidotes and Understanding of poisonous creatures. Treatment include herbals, administered as nasal drops, eye drops and oral medicine, strict food regulations, Abstaining from alcohol and non vegetarian foods. Treatment also includes rituals and offerings to God.Tribal Information from Kerala.The Kani tribe of the Western Ghats of Kerala apply ‘Vishakallu’, a medicated stone with anti - poisoning properties to the affected area (snake bite). The ingredients that go into the making of ‘Vishakallu’ are, Pebbles from the river, Tulsi or Holy Basil leaves (Ocimum sanctum - Lamiaceae), Leaves of Perumthumba (Anisomeles malabarica - Lamiaceae), Heartwood of Chandanam (Santalum album - Santalaceae).
Mode of preparation of ‘Vishakallu’
Pebbles are ground, mixed with the other ingredients and made into paste and wrapped with 7 leaves of Aristolochia tagala. It is baked on fire made by burning wood of Chuvannakil (Chukrasia tabularis – Meliaceae; native to India and Sri Lanka ) or Dysoxylum malabaricum (Vella Akil; Meliaceae), sandalwood, holy basil and camphor. This baked cake is covered with paste of termite mount soil and again baked on low fire. The soil coat is removed and the cake is soaked in water for an hour, covered with paste of Pittosporum neelgherrense - Analivegam ( Pittosporaceae) stem bark . The whole thing is baked again and covered with stem bark of Kunstelaria keralensis (Fabaceae). And sun dried. This ‘stone’ is stored in burnt cow dung ash and Nicotiana tabacum - Pukayila (Solanaceae) leaves (Tobacco).
Mode of administration of ‘Vishakallu’
It is administered only by experienced tribal healers. The stone is directly applied to the bitten part. It sticks there and absorbs the venom from the wound. During this operation, Lord Siva is propitiated by chanting mantras. When all the venom is absorbed the stone falls away automatically. The stone is immersed in cow’s milk for detoxification for 2 hours.It is again dried and stored in cow dung ash. It is believed from experience that it can be used 20 times.
Take home message
This patient had life threatening complications due to the dalayed medical treatment.People sought Visha kallu treatment initaily