Skill Page - Safe Injection Practices
30 JAN 2015
Safe Injection Practices
Ms Remya Dasan, EMN
.bmp)
INTRODUCTION
Giving injections is a regular and common place activity for nurses, and good injection technique can make the experience for the patient relatively painless. However, mastery of technique without developing the knowledge base from which to work can still put a patient at risk of unwanted complications
OBJECTIVE
- Identify the safe anatomical sites for ID, SC and IM injections.
- Locate the specific muscles for IM injections and explain the rationale for their use.
- Give sound reasons for your method of skin preparation.
- Discuss ways to reduce patient discomfort during an injection.
- Describe the nursing care a patient requires to avoid complications associated with injections
BEST INJECTION PRACTICES
- Hand washing
- Selection of device
- Sterile preparation of medicine
- Site selection
- Cleaning of site
- Safe administration of medicine
- Safe disposal of waste
- Documentation of procedure
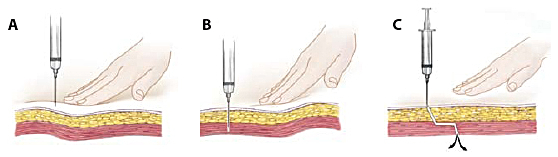
INTRADERMAL INJECTION
The intra dermal route provides a local, rather than systemic, effect and is used primarily for diagnostic purposes such as allergy or tuberculin testing, or for local anesthetics.
This layer underneath the epidermis, is highly vascularized and contains large amount of immune cell
HOW????????
- Pre procedural preparations
- Insert the needle at an angle parallel to long axis for about 2mm,so that entire needle bevel penetrates the skin and the injected solution raises a small bleb.
- Take it away leave the site uncovered.
SITE???
.bmp)
SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
- The subcutaneous route is used for a slow, sustained absorption of medication, up to 1-2ml being injected into the subcutaneous tissue.
- In adult maximum volume for subcutaneous injection is 3ml.
- Don’t massage the area after giving heparin and insulin
HOW?????
- Pre procedural preparation
- Pinch up the skin between thumb and fore finger ,so as to lift the adipose tissue.
- Push the needle in the pinched up tissue at 45 degree angle.
- Use 1 ml syringe.
SITE???
.bmp)
INTRA MUSCULAR INJECTION
- Intramuscular injections deliver medication into well perfused muscle, providing rapid systemic action and absorbing relatively large doses.
- The maximum volume of medication can be administered for an adult patient is 3 ml , in children it is half.
Up to 2ml
.bmp)
Up to 3ml
.bmp)
2ml or less
.bmp)
Up to 3 ml
.bmp)
Z- tack technique
The Z track technique was initially introduced for drugs that stained the skin or were particularly irritant. It is now recommended for use with the full range of IM medications and is believed to reduce pain, as well as the incidence of leakage
ASPIRATION
Aspiration no longer recommended for SC Injection , it should be practiced IM Injection
Twelve point for painless injection
- Prepare patients with appropriate information before the procedure.
- Change the needle after preparation of the drug and before administration to ensure it is clean, sharp and dry, and the right length
- Make the ventrogluteal site your first choice, to ensure that the medication reaches the muscle layer
- Position the patient so that the designated muscle group is flexed and therefore relaxed
- If cleaning the skin before needle entry, ensure skin is dry before injecting
- Consider using ice or freezing spray to numb the skin before injection, particularly in young children or needle-phobic patients
- Use the Z track technique
- Rotate sites so that right and left sites are used in turn, and document rotation
- Enter the skin firmly with a controlled thrust, positioning the needle at an angle as near to 90° as possible, to prevent shearing and tissue displacement
- Inject medication steadily and slowly
- Allow ten seconds after completion of injection to allow the medication to diffuse and then withdraw needle at the same angle as it entered
- Do not massage the site afterwards, but be prepared to apply gentle pressure with a gauze swab
INTRAVENOUS INJECTION
Most often it was administered through a peripheral / central venous line
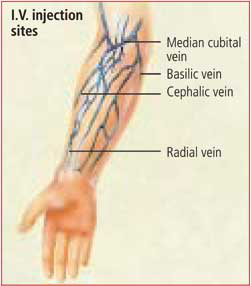
Steps
- Prepare tray (injection tray , kidney tray , gauze pieces , germiclean , micro shield.
- Prepare iv medication , take the medication from bag remove the cover of syringe.
- Aspirate the medication from ampule / vial – if it is powder form dilute appropriate diluent .
- Kept injection tray and prepare iv flush also.
- Note: if the line is not use flush every 6 hourly with normal saline.
CONCLUSION
Giving an injection safely is considered to be a fundamental nursing activity, and yet it requires knowledge of anatomy and physiology, pharmacology, psychology, communication skills and practical expertise.
Recent skills
- Skill Page - Lasix infusion
- Skill Page - Cervical Collar
- Skill Page - Triage
- Skill Page - Female Catheterization
- Skill Page - Catheterisation
- Skill Page - Braden Scale
- Skill Page - Safe Injection Practices
- Skill Page - Basics of ECG
- Skill Page - SOLUMEDROL INFUSION
- Skill Page - Oxygen Therapy